Seaweed Research Trends to Watch in 2023
Harvesting seaweed responsibly has the potential to address some of the world’s biggest sustainable development challenges through nature-based solutions. Owing to its favorable characteristics (such as binding properties, etc. – Source), Seaweed innovations have been increasingly adopted in various industries. Seaweed is already widely used in the food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and agriculture industries and has potential as a biofuel.
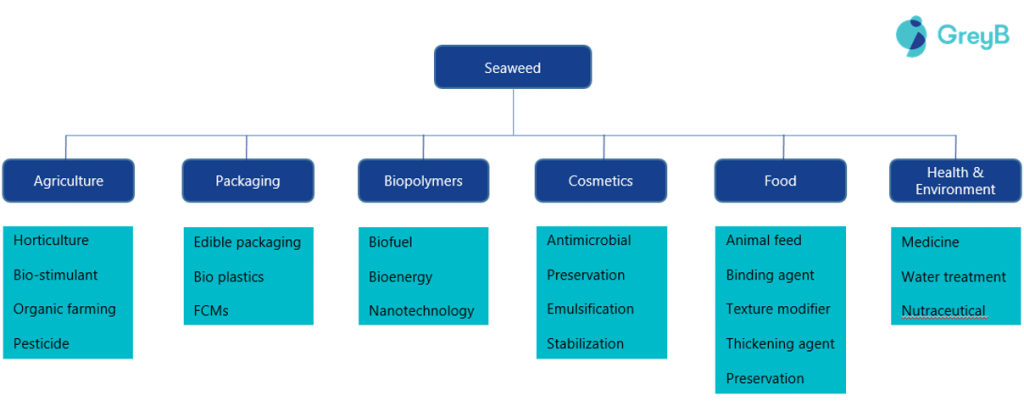
Through the report, we walk you through various seaweed innovations and the challenges they face in various industries. We will be talking about Seaweed Innovation in 3 application areas. However, if you are interested in Seaweed Innovation in all 6 application areas, download the complete report by filling out the form below:
What is the present status of Seaweed Innovation in the world?
Seaweed is available in abundance, and before heading over to the seaweed innovations happening in various industries, let us look at the quantity that is present for use.
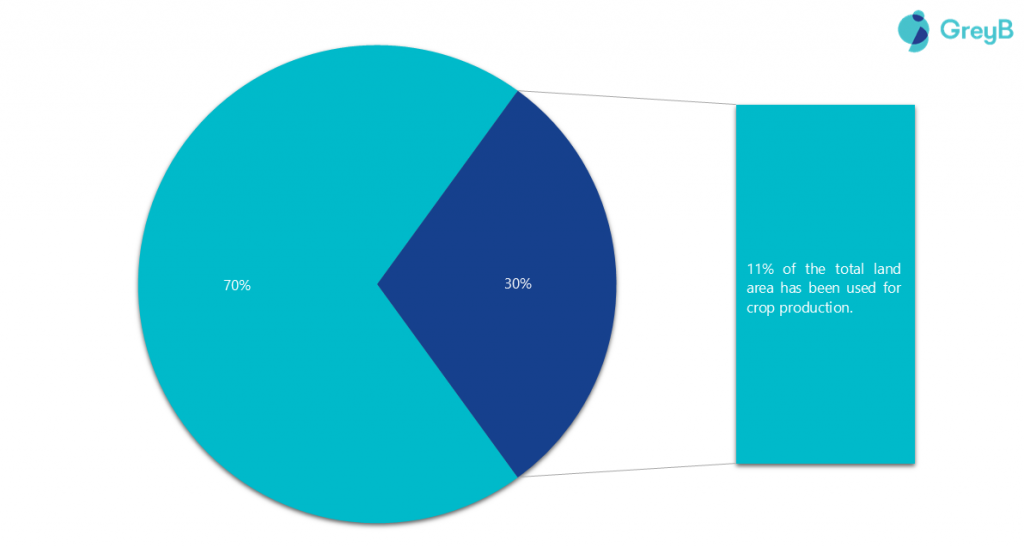
- 70% of the world’s surface (ocean) has not traditionally been used for crops, and it is 11% of the land that is brought to use for crop production.
- Seaweed has amazing carbon dioxide uptake and storage capability. Kelp takes in five times more carbon than most land-based plants.
- Seaweed needs no fertilizing, no weeding, and no watering. Also, it has very few enemies in the form of pests or diseases.
In short, Seaweed’s availability negates the challenge of being a limited resource. So the question arises: what is the status of seaweed production and investments happening presently? The next section talks just about that.
Global Seaweed Production & Investments
The Seaweed Market is expected to reach $23.2 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2021 to 2028. Also, in terms of volume, the seaweed market is expected to record a CAGR of 9.5% from 2021 to 2028 to reach 11,408.3 KT by 2028.
The growing market share is one of the reasons 2021 saw a big jump in seaweed startup investments, especially outside Asia.
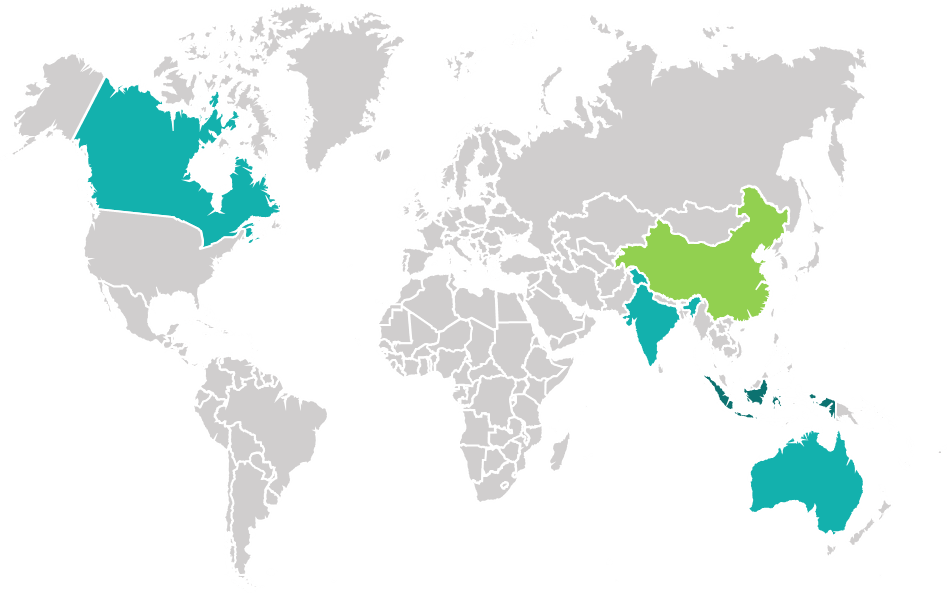
China and Indonesia have 80% of the global seaweed market share. (Source). Collectively, Asian countries own more than 90% of seaweed’s global market share.
In Asia, apart from China and Indonesia, India is also a considerable market for seaweed. Even India knows that. That’s why the government of India is investing ~$87m in seaweed cultivation. Also, a seaweed farming initiative is being launched, promising 30,000 tons of seaweed per year.
In the Pacific, Australian Seaweed Institute’s blueprint plans ~$8m R&D investment for the seaweed industry. (Source)
Commercial Applications of Seaweed
Globally, the use of seaweed is increasing in various downstream industries due to its various favorable properties (such as edible, low carbon footprint, emulsifier, etc.). Now, let’s explore these application areas to see the innovations happening in this domain.
Seaweed Innovation in Food
Challenges Related to Seaweed in “Food”
Seaweed has been a staple food source in many cultures for centuries. As people become more aware of the relationship between diet and health, consuming seaweed has been and is increasingly gaining attention. Nowadays, many new food products based on seaweed have been developed and marketed, offering enhanced health benefits and the potential to decrease the risk of diseases.
However, despite their excellent properties (such as nutritional, physicochemical, and textural properties), seaweeds are far from being regarded as a commodity, and this is mainly due to their low processing suitability. Below are the major challenges hindering its adoption in the broader domain:
- Undesirable taste and texture properties of the final seaweed product
- Inconsistent dispersibility and viscosity
- Low-strength seaweed gels reduce the usefulness of seaweed-based flour.
- Deterioration in nutritional benefits after processing
A seaweed-based product that preserves the nutritional, physicochemical, and health benefits of unprocessed seaweeds and has superior rheological properties is of great commercial interest.
- A seaweed gel having an optimum strength would make the usage of seaweed-based flour widespread.
- The solution should be a natural, i.e., non-chemically modified, seaweed-based product that overcomes these challenges.
Companies and Startups Researching in Seaweed-Based Food

Cargill’s Seaweed Powder
In 2021, Cargill unveiled its first seaweed powder offering, marketed as “WavePure ADG 8250”. The product is claimed to have limited color and flavor deviation properties in the final product. It also has smooth and creamy textures in dairy, offering gel and thickening properties.
The innovation launch is consistent with a patent filed by Cargill.
Cargill filed a patent application, US20210000896A1, in 2019 that claims to effectively overcome the seaweed’s usage limitations (preserving the nutritional, physicochemical, and health benefits while giving superior rheological properties) in the food industry.
Key highlights of the seaweed-based product from Cargill:
- The seaweed biomass is dried to a moisture level of at most 40 wt% and then cooked in a brine solution.
- A natural salt (such as guar gum, alginate, agar, etc.) is mixed with seaweed.
- This composition allows the alteration of the properties of products (rheological properties). This enables the designers of such products to simplify the properties of their recipes.
Seaweed Innovation in Packaging
Challenges related to Seaweed in “Packaging”
Globally, all industries are rushing to align themselves to incorporate sustainability in their businesses. Due to this, biodegradable products (for packaging) have been touted as a potential solution. In an attempt to address this issue, various biodegradable materials are being researched to reduce the future environmental impact. But, due to their low strength, rigidity, and expensive recycling process, their usage is limited.
To overcome this, using polysaccharide-based materials (derived from seaweed) might present an eco-friendly technological solution for packaging. But there are the following challenges in the use of seaweed in packaging –
- The complex and energy-intensive recycling process of seaweed-based packaging
- Mass production of seaweed
- Expensive processes for extracting seaweed-based raw materials
- The problem of contamination when not handled correctly while recycling
Startups Working on Seaweed

Notpla’s Biodegradable & Edible Packaging
In 2019, Ooho (Notpla’s product based on seaweed-derived packaging material) was trialed at the London Marathon. The runners were offered the sachets, which were filled with a sports drink.
This trial resulted from a four-way project between Hellmann’s, Just Eat, Innovate UK, and Notpla. The company has secured funding from the UK Government’s innovation agency (Innovate UK)
Also, Unilever, Just Eat, and Notpla have partnered to launch sauces in seaweed sachets. Following several trials and early-stage partnerships with brands such as Lucozade and Just Eat, Notpla is now looking for more manufacturing partners. Notpla will focus on selling commercially and more widely, with plans to expand across Europe and into the US soon. (Source) (Source)
Notpla has also patented this seaweed-based technological innovation.
Notpla filed a patent application, EP3601061A1, in 2018 that claims to have innovated an alginate-based edible and biodegradable packaging film.
Key highlights of the alginate-based product from Notpla:
- The packaging film comprises cross-linked alginate (derived from seaweed), manufactured using calcium ion solution.
- The cross-linked alginate reduces water and oil permeability and increases mechanical strength.
- The process can be worked upon at room temperature, so no special environmental conditions are required, thus making the process economical.
Seaweed Innovation in Health & Environment
Challenges related to Seaweed in “Water Treatment”
Wastewater is a by-product of any [mostly industrial] process or activity. It could be from manufacturing industries, factories, landfills, households, textile industries, petrochemical industries, aquaculture, agriculture, etc. With the high-standard requirements set by environmental regulations on wastewater discharge, wastewater treatment has gained attention worldwide.
Green solutions (without chemicals) that are effective in their operations and are also environmentally friendly are of great commercial interest. While there is interest in moving towards green solutions, there are certain challenges that need attention while adopting green materials like seaweed –
- Improper heavy metal filtration capabilities of green chemicals
- Low filtration capabilities
- The presence of salts affects the performance properties of green solutions.
- Restricted applications in various downstream industries
Inadequately treated or untreated wastewater greatly contributes to releasing unwanted toxic contaminants into water bodies. Some of these contaminants are persistent and bio-accumulative, becoming a great concern as they are released into the environment.
To address this problem, processes that use activated carbon, graphene, or carbon nano-tubes are being developed, as carbon-based processes can help remove dyes and heavy metals through adsorption.
Thus, there is an urgent need to make the carbon-based cleaning process fully green, and seaweed-based materials might be the answer.
Seaweeds are known as carbon sinks. The nanocomposite obtained from seaweed has shown very high adsorption capacity for various cationic and anionic dyes, lead, and chromium.
Companies and Universities Working on Seaweed-Based Water Treatment

CSIR & IIT’s Seaweed-Based Water Treatment
Researchers at the Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute have jointly developed (with the Indian Institute of Technology) a carbon-based cleaning process. The process is completely environment-friendly and uses seaweed as the starting material. They have synthesized graphene-iron sulfide nanocomposite from abundantly found seaweed (Ulva fasciata) through the direct pyrolysis technique.
This nanocomposite was also tested by depositing it on a commercial filter paper and used in a customized flow cell in continuous filtration mode. It was able to render highly toxic black dye solution into colorless water.
A maximum adsorption capacity of 645 mg per gram for the lead was achieved at neutral pH. Scientists have claimed this is the highest ever reported for any biomass-derived carbon material in their study (published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials). It could also remove highly toxic hexavalent chromium from wastewater.
Key highlights of Seaweed-Based Water Treatment:
- Solvent-free route for the production of graphene-nanocomposite has been proposed.
- Iron doping plays a dual-faceted role in exfoliating as well as activating agents.
- This composite exhibits high adsorption capacity for Pb2+ (645 ± 10 mg/g) and Cr (IV).
- This composite shows the excellent removal ability of dyes with good recyclability (8 cycles).
- Suitable for membrane coatings and fabrication applications.
Conclusion
Seaweed is a material that can be employed by multiple industries, and this opens the doors to seaweed innovation. That’s why so many companies, startups, and research institutes are researching it for different purposes. If you also want to explore various seaweed innovations for probable growth, we can help you establish a footing in the industry.
Authored by: Ambuj Chaudhary, Landscape Team.





