Exam practice
GCSE Combined Science: exam-style questions
Free online AQA Synergy foundation/higher science tests based on past papers to increase your understanding of biology, chemistry and physics GCSE exams.
GCSE Combined Science: quick-fire questions
Free interactive quiz questions based on AQA Synergy GCSE combined science past papers to help you prepare for your biology, chemistry and physics GCSE exams.
Podcasts
Atomic structure and the periodic table
Learn about atomic structure and the periodic table for your GCSE chemistry exam, with Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea.

Bonding, structure and properties
Learn about bonding, structure and properties of matter for your GCSE chemistry exam, with Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea.

Chemical changes
Dr Sunayana Bhargava and Tulela Pea take you through what you need to know about chemical changes for your GCSE chemistry exam.

Forces
Learn all about forces for your GCSE physics exams, with scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer.

Electricity
Scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer guide you through the key facts about electricity for GCSE physics.

Energy
Learn all about energy for your GCSE physics exam, with Ellie Hurer and James Stewart.

The Cell
All living things are made of cells, which is why they’re called the building blocks of life.

The organisation of plants and animals
Learn all about plant and animal organisation with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Infection and response
Learn all about infection and response for your GCSE biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Homeostasis
Learn all about homeostasis for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Inheritance, variation and evolution
Learn all about inheritance, variation and evolution for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Ecology
Learn all about ecology for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Science exam techniques
Learn all about science exam techniques for your GCSE science exams with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Building blocks
States of matter - AQA Synergy
Matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Atoms can exist on their own or together as molecules. Atoms are very small and around 100,000,000 of them end to end would measure one centimetre.
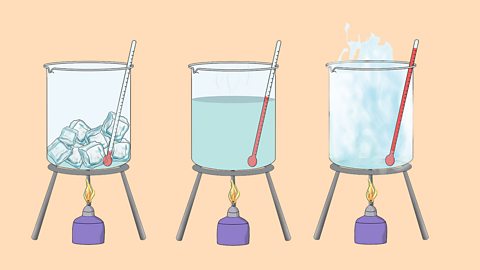
Atomic structure - AQA Synergy
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated from its atomic number and mass number.

Cells in animals and plants - AQA Synergy
Organisms are made up of cells. Most organisms are multicellular and have cells that are specialised. Microscopes produce magnified images of cells.

Transport into and out of cells - AQA Synergy
For an organism to function, substances must move into and out of cells. Three processes contribute to this movement – diffusion, osmosis and active transport.

Cell division - AQA Synergy
There are two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. Meiosis produces four non-identical haploid gametes (sex cells).
Waves - AQA Synergy
Waves are one way in which energy may be transferred between stores. Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves will transfer energy without matter being transferred.
Sample exam questions - building blocks - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Transport over larger distances
Quiz: Photosynthesis activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying factors affecting photosynthesis and interpreting photosynthesis test results.

Quiz: Photosynthesis activity 2 (higher)
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying interpreting photosynthesis test results, and distance and light intensity.

Quiz: Respiration activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, oxygen debt, and metabolism.

Quiz: Respiration activity 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, oxygen debt, and metabolism.

Respiration - AQA Synergy
All living cells respire. This process releases the energy stored in glucose for life processes. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen, whilst anaerobic respiration occurs without it.

Exchange surfaces and transport systems - AQA Synergy
Most animals and plants consist of different types of cells organised as tissues, organs and systems. The human respiratory system is a body system adapted for efficient gas exchange.

The digestive system - AQA Synergy
The major nutrients required for a healthy diet are carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. The digestive system breaks down large molecules of food, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream.

Coordination and control - AQA Synergy
The nervous system enables humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour. The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream from glands throughout the body.

Plant organisation - AQA Synergy
Plant cells, tissues and organs are adapted to their functions. The stem, root and leaves form an organ system that transports substances into, around and out of a plant. The leaves are the main organ of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis - AQA Synergy
Plants use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen during photosynthesis.

Plant diseases - AQA Synergy
Plants can become infected with pathogens such as the tobacco mosaic virus and the rose black spot fungus.

Sample exam questions - transport over larger distances - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Interactions with the environment
Lifestyle and health - AQA Synergy
Health is the state of physical, mental and social well-being. It is not just being free from disease. Communicable diseases can be transferred from one person to another, whilst non-communicable diseases cannot.
Homeostasis - AQA Synergy
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment. Regulating body temperature, blood glucose level and water content are all examples of homeostasis.
Reproduction and fertility - AQA Synergy
Hormones are secreted by glands in the endocrine system. They are involved in puberty, regulating the menstrual cycle, contraception and fertility treatments.

Radiation and risk - AQA Synergy
There are many different types of radiation. Some are dangerous and some can be useful, it is important to understand the risks posed by all types of radiation.
Preventing, treating and curing diseases - AQA Synergy
Some diseases can be treated with antibiotics, but not all can be cured. Vaccinations allow protection against specific diseases, but the level of protection depends on the amount of people vaccinated.
Sample questions - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Explaining change
The atmosphere - AQA Synergy
The early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and water vapour. Human activities are releasing greenhouse gases which are causing global warming, and other atmospheric pollutants.

Water - AQA Synergy
The water cycle describes how natural processes move water between living and non-living stores. All humans rely on safe drinking water. Water is purified to remove insoluble and soluble substances. Salt can be removed from sea water to make it safe to drink. Waste water must be treated before being released into the environment.

Ecosystems and biodiversity - AQA Synergy
An ecosystem is the living organisms in a particular area together with the non-living components of the environment, such as soil, air and water. An ecosystem is biodiverse if it contains many different species.

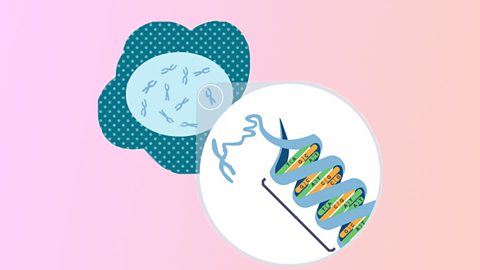
Inheritance - AQA Synergy
Inheritance is the process of passing genetic information to offspring. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a protein. Inheritance of genes can be shown in Punnett square diagrams.
Evolution - AQA Synergy
Evolution is the change of inherited characteristics within a population over time through natural selection, which may result in the formation of a new species.

Sample exam questions - explaining change - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Building blocks for understanding
Quiz: Calculations in chemistry (Higher)
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying the mole, calculating concentrations, limiting reactants, and mole calculations.

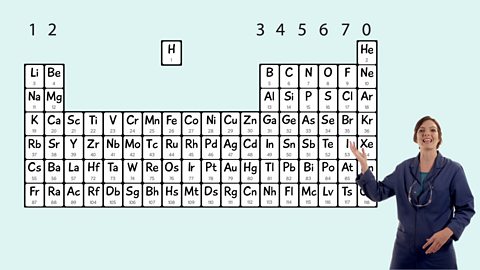
The periodic table - AQA Synergy
Mendeleev made an early periodic table. In the modern periodic table, elements are in order of atomic number in periods and groups. Electronic structures model how electrons are arranged in atoms.

Groups in the periodic table - AQA Synergy
Elements in the same group of the periodic table show trends in physical properties, such as boiling point. They have the same number of electrons in their outer shell, so they are similar in their chemical properties.

Chemical equations - AQA Synergy
Chemists use symbols and formulae to represent elements and compounds. Word equations and balanced chemical equations represent the changes that happen in chemical reactions.
Calculations in chemistry - AQA Synergy
Relative formula masses can be calculated and used in conservation of mass calculations. Calculations can be carried out to find out concentrations of solutions.

Sample questions - Building blocks for understanding - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Interactions over small and large distances
Quiz: Magnetic fields
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE combined science students studying poles of a magnet, induced and permanent magnetism, and detecting and drawing magnetic fields.

Forces - AQA Synergy
Forces are responsible for all the interactions between particles and objects. They can be divided into two categories: contact forces and non-contact forces.

Energy changes - AQA Synergy
Energy is a key principle in physics. Forces cause changes and energy calculations allow us to measure how much change can happen.

Ionic compounds - AQA Synergy
An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions. It has a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction.

Covalent bonding - AQA Synergy
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonding results in the formation of molecules or giant structures. Substances with small molecules have low melting and boiling points and do not conduct electricity. Giant covalent substances have very high melting points.

Metals - AQA Synergy
Metals have giant structures of atoms with delocalised electrons. This explains their high melting and boiling points and why they conduct electricity.

Magnetism and electromagnetism - AQA Synergy
Magnetism is due to the magnetic fields around magnets. The fields can be investigated by looking at the effects of the forces they exert on other magnets and magnetic materials.
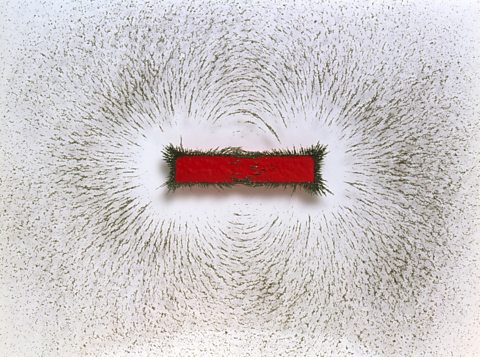
Sample questions - interactions over distances - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Movement and interactions
Motion - AQA Synergy
The movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values. These are both used to help in the design of faster and more efficient vehicles.

Newton's laws - AQA Synergy
Forces cause changes in the motion of an object. Newton’s Laws help us to understand and analyse those changes. Unbalanced forces cause changes in speed, shape or direction.

Circuits - AQA Synergy
Electrical current transfers energy around circuits. There are two types of current: direct and alternating.
Mains electricity - AQA Synergy
Electricity can flow either as direct or alternating current, and is used in homes to power electrical appliances. The National Grid distributes electricity throughout the country.

Acids and alkalis - AQA Synergy
Indicators are used to determine whether a solution is acidic or alkaline. Acids react in neutralisation reactions to produce salts.

Rates of reaction - AQA Synergy
The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate. Temperature, concentration, pressure, particle size and the use of catalysts all affect reaction rate.

Energy, rates and reactions - AQA Synergy
Energy changes can be represented using energy profiles. Catalysts (including enzymes) speed up chemical reactions. Energy changes can be calculated from bond energies.

Equilibria - AQA Synergy
Some chemical reactions can be reversed. Reversible reactions can reach a dynamic equilibrium. Changing the conditions can change the amount of product made.

Electrons and chemical reactions - AQA Synergy
The reactivity series shows metals in order of reactivity. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive ions. Electrolysis can be used to split ionic compounds and to extract metals.

Sample exam questions - movement and interactions - AQA Synergy
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Guiding Spaceship Earth towards a sustainable future
Carbon chemistry - AQA Synergy
Pure carbon can be found as diamond, graphite, fullerenes and graphene. Crude oil is made from hydrocarbons which can be processed to make a variety of fuels and other useful products.

Material resources - AQA Synergy
Metals and other useful resources can be extracted from the Earth's crust. Life cycle assessments measure the environmental impact of a product over its entire life. Recycling helps to conserve energy and resources.

Energy resources - AQA Synergy
Every person, animal and device transfers energy. Much of that energy is supplied by electricity, which must be generated from other energy stores. Some of these are renewable but most are non-renewable.

Sample questions - guiding Earth towards a sustainable future - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Practical skills
Practical skills for carrying out a scientific investigation
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription