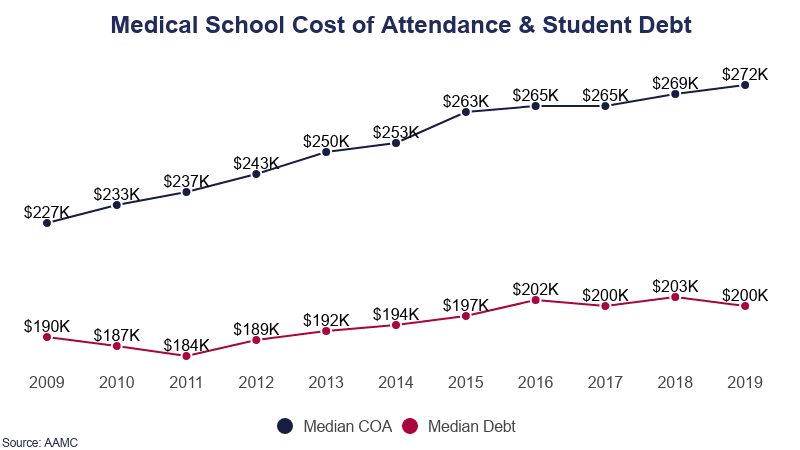
Report Highlights. The average medical school debt is $202,453, excluding premedical undergraduate and other educational debt.
- The average medical school graduate owes $250,995 in total student loan debt.
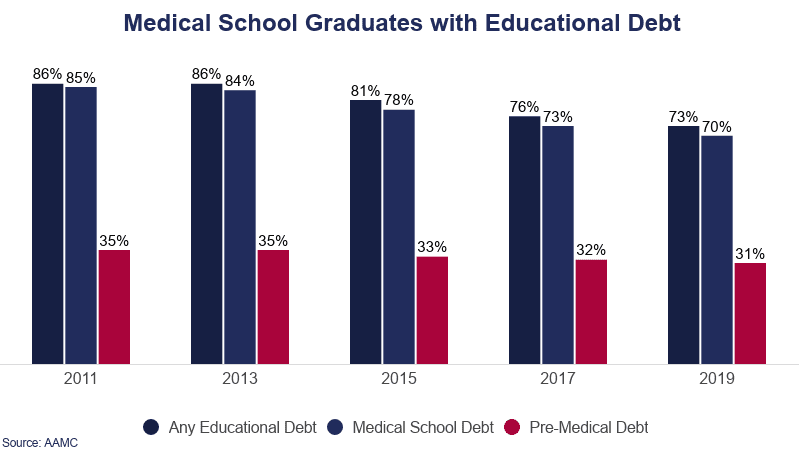
- 73% of medical school graduates have educational debt.
- 31% of indebted medical school graduates have premedical educational debt.
- The average medical school graduate owes 4 times as much as the average college graduate
- 70% of medical school students use loans specifically to help pay for medical school (as opposed to undergraduate or premed debt).
Related reports include Student Loan Debt Statistics | Average Cost of College | Average Law School Debt | Average Time to Repay Student Loans | Student Loan Default Rate | Student Loan Refinancing
Medical School Debt Statistics
Between medical school and undergraduate study, physicians must pay for 8 years of postsecondary education before they can work as doctors.
- Medical school graduates owe a median average of $215,100 in total educational debt, premedical debt included.
- Indebted medical school graduates who received more than $100,000 in scholarships owe a median average of $115,000 if they attended a public institution and $130,000 if they attended a private medical school.
- An average medical school graduate owes more than 6 times as much in educational debt as an average college graduate.
- A 156% increase in the average debt took just over 15 years.
- Adjusted for inflation, the cost of medical school has nearly doubled, increasing by 372%.
- 12.4% was the annual growth rate of medical school debt.
- 2.5% was the annual growth rate of the cost of medical school.
- In Canada, the average medical school debt among graduates is US $19,250.
- If debt continues to outpace the cost of attendance at the present rate, the average medical student debt will exceed $300,000 by 2024.
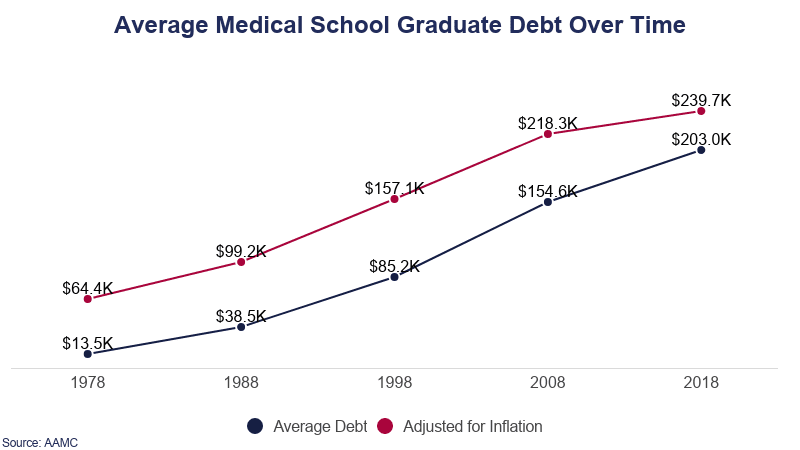
Historical Medical School Debt
The average medical graduate’s debt rate outpaces the inflation of academic costs, which in turn outpaces economic inflation.
- In 1978, the average medical school debt in the U.S. was $13,500.
- That’s $53,648 when adjusted for inflation.
- Medical school graduates in the 1999-2000 academic year owed $87,000 in educational debt.
- Adjusted for inflation, the average debt for a medical school graduate was $124,700.
- Graduates owed an average of $122,270 for medical school alone in 2000.
- That’s $118,416 when adjusted for inflation.
- $246,340 was the average medical school debt owed by 2016 graduates.
- In 2010, 86% of medical school students graduated in debt.
- By 2017, 75% of medical students graduated with debt.
- Between 2010 and 2017, the rate of individuals with debt decreased by 11%.
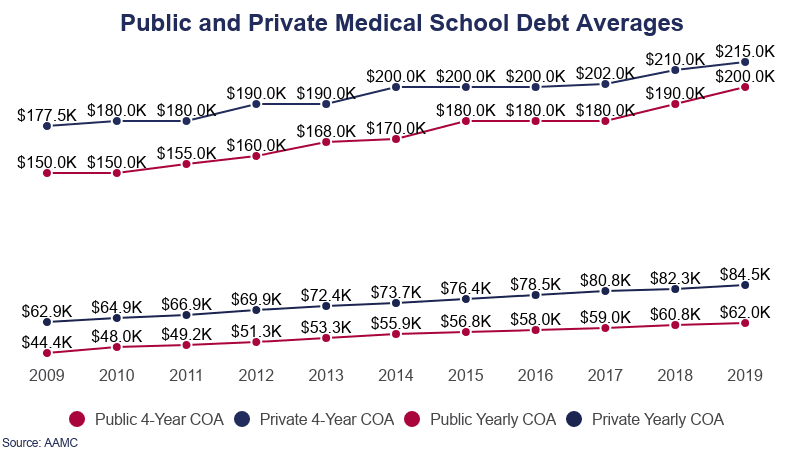
Public vs. Private Medical School Debt
The cost of attendance for a private medical school is higher than that of a public medical school. The rate of the debt increase, however, is not equal to the increased cost of attendance.
- Public medical school graduates owe $15,000 less on average than private medical school graduates.
- $200,000 was the median student debt among private medical school graduates in 2016; the cost of their education was $306,171.
- $180,000 was the median student debt among public medical school graduates; $232,838 was the cost of their education.
- Private medical school graduates leave school owing 65.1% of their cost of attendance.
- Public medical school graduates leave school owing 79.9% of their cost of attendance.
- In 2009, private medical school graduates owed 73.8% of their cost of attendance.
- Also in 2009, public medical school graduates owed 89.7% of their cost of attendance.
Loan and Repayment Statistics
Some institutions have responded to the student debt crisis with more scholarships and loan forgiveness programs. Not everyone benefits from these programs, however, leaving some students to face increasing debt even as they continue to make payments.
- The average physician ultimately pays $135,000 – $440,000 for an educational loan plus interest.
- $135,000 – $254,000 is just from interest.
- A $200,000 debt can double in 10 years at current interest rates, even with regular payments.
- An average of 33% of indebted medical school students owe repayments on Perkins or disadvantaged student loan programs.
- 6.54% is the interest rate on the average federal direct unsubsidized loan for graduate or professional borrowers.
- $2,275 is the minimum monthly payment the average medical school graduate must make in order to pay off all educational debts within 10 years.
- Including interest, $346,008 is the graduate’s grand total pay-off.
- If the average physician can’t pay off educational debts within 10 years, their total educational costs will likely exceed $300,000.
- The medical school loans alone require 120 monthly payments of $1,951.
- In the late 1980s, 59.9% of indebted medical school graduates had Health Professions Student Loans.
- By 2000, just 4.4% of indebted students had HPS loans; reports indicate that little-to-no funds are being allocated to the HPSL program.
Medical School Debt & Socioeconomics
Students who come from families with a good deal of wealth accrued are more likely to attend medical school than those without. Low-income students are attending medical school at decreasing rates, possibly due to the specter of debt.
- 45.2% of medical school students cite their ability to pay off debt as a primary concern.
- Low-income attendees declined by 34% in medical schools in Ontario, Canada.
- Since 1997, fees at these schools have increased 116%.
- In the United States, 50% of low-income graduates have medical school loan debt that exceeds $100,000.
- Among those with debts that exceed $200,000, those with Perkins or disadvantaged student loans are the majority.
- Among students entering medical school, 14.5% had debts unrelated to their education.
- Among those, 58.2% had less than $10,000 in debt unrelated to their education.
- 11.2% had noneducational debts exceeding $100,000.
| Demographic | Share with Student Debt | Median Student Debt |
|---|---|---|
| American Indian and Alaska Native | 80% | $212,375 |
| Asian, not Hispanic | 61% | $180,000 |
| Black, not Hispanic | 91% | $230,000 |
| Hispanic | 75% | $200,000 |
| White, not Hispanic | 71% | 200,000 |
Medical School Debt Demographics
Financial struggles affect demographics to varying degrees. Sociologists, economists, and behavioral scientists agree that the root causes of financial disparities are social or socioeconomic factors.
- Male medical school graduates are 34.2% more likely than female graduates to leave school in debt.
- Among U.S. citizens, Black and African American medical school students owe more, on average, than their peers of any other race or ethnicity.
- 50% of Black medical school graduates are more than $200,000 in debt.
- 17.1% have debts of $300,000 or more.
- Asian students attending public medical schools have the second-lowest average debt balance.
- Students of unknown or unspecified race attending public schools graduated with the least amount of debt.
- Non-citizens and residents who graduated from public medical schools have the greatest amount of average debt.
- Black or African American graduates who attended private medical schools have the second-highest amount of debt.
Medical School Tuition and Fees
Just applying to medical school costs thousands in entrance exam fees, preparation courses, travel & interview expenses, transcript processing fees, etc. The price of medical school has increased at more than twice the rate of currency inflation; this has been a significant contributing factor to the rise in medical school graduate debt.
- $58,500 is the average cost of tuition and fees for a first-year medical student in 2020.
- $16,900 was the total cost of tuition and fees for the average first-year medical student in 2000.
- Adjusted for inflation, that’s $25,500.
- The cost of medical school increased 91% in 22 years, even after adjusting for inflation.
- During that time, the cumulative rate of inflation of the U.S. dollar was 50.5%.
- $2,800 is the average cost of medical school application fees alone.
- $10,000 is the application budget recommended by academic counselors.
- 69% of medical school students use loans to help pay for school.
- In the U.S., 131 institutions award over 18,000 medical degrees each year.
- 55,188 unique applicants submitted a total of 990,790 applications to medical schools for the 2021-2022 academic year.
- 22,712 applicants were accepted in 2022.
- 40% of those accepted were from out-of-state.
Sources
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), List of Current Digest Tables
- Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), Table: U.S. Medical School Applications and Matriculations by School
- CNBC, Here’s How Much Medical Students Are Paying Just to Get Into School
- National Library of Medicine (NLM), Effects of Rising Tuition Fees On Medical School Class Composition and Financial Outlook
- NLM, A Retrospective Analysis of the Relationship Between Medical Student Debt and Primary Care Practice in the United States
- AAMC, Applicant, Matriculant, & Graduation, by Medical School Tables
- Calculator.net, Financial Calculators
- CPI Inflation Calculator
- AAMC, Trends in Cost and Debt at U.S. Medical Schools Using a New Measure of Medical School Cost of Attendance
- U.S. Department of Education (ED) Office of Federal Student Aid (OFSA), Understand How Interest is Calculated and What Fees are Associated with Your Federal Student Loan
- AAMC, Matriculating Student Questionnaire, 2019 All School Summary Report 2020
- AMA, Physician Education Debt and the Cost to Attend Medical School: 2020 Updated
- AAMC Tuition and Fees Report
- Total Graduates by U.S. MD-Granting Medical School and Gender, 2017-2018 through 2021-2022
- Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2021 All Schools Summary Report